Technical Terms related to Warranty Claims
-
Water entering the property through the structure (walls, roof etc) but not from leaking pipework or other sources. Most often it will consist of staining to the decorative surfaces.
-
This happens when warm, moist (humid) air contacts a cold surface, such as an internal wall. The water vapour in the air then turns into beads of moisture, which can lead to mould and mildew growth, damage to walls and ceilings, and health issues. It can be caused by lifestyle issues such as drying clothes internally, closing off all ventilation or excessive use of bathing and cooking facilities.
-
Condensation in lofts occurs when humid air makes its way into the loft space and hits a cooler surface leading to beads of moisture on timbers, lintels and on the underside of the roof. Often associated with bathroom extractor fans which vent via the loft.
-
Any part of the building that is an active structural element of the building, i.e., by bearing the weight of other elements, fixtures or people. Also applies to wind, snow and other weather-related loadings.
-
A wall, normally either a single leaf or two leaves to form a cavity wall constructed from bricks or blocks normally bonded with lime mortar or sand/cement mortar. This type of wall is normally load-bearing.
-
A stud wall comprises a frame of timber or metal studs secured to the floor, ceiling and walls, which is then covered with plasterboard. These walls are generally not load-bearing but can be.
-
Timber frame is a more recent method of building that relies on a timber frame as the means of structural support. Externally they can be finished in masonry, render or cladding.
-
The dividing wall between two adjoining properties.
-
Item rendering refers to the process of applying a coat of sand/cement, polymer, or other proprietary render systems on the external walls of a property to make them smooth or textured as desired.
-
Cladding is the installation of one material over another to provide an outer skin or layer. Cladding can be of various materials and can provide thermal and/or weather resistance or be just for aesthetic reasons.
-
A roof which is predominantly flat or with a pitch (slope) of less than 10 degrees. They can be covered in felt, asphalt, or membranes.
-
Green roofs are roofs that are partially or completely covered with plants and vegetation. These can also be known as sedum roofs, grass roofs or living roofs.
-
A flat roof which is designed to allow collection and controlled discharge of rain fall.
-
A sloping roof greater than 10 degrees, most commonly covered in slates or tiling made from concrete or clay.
-
The triangular section of wall supporting two sides of a sloping roof. The term also applies to the whole end wall of a building.
-
A pitched roof where one or more of the sides slopes downwards from a peak and there are no gable walls.
-
A low wall along the edge of a roof or terrace which is the upward extension of the wall below.
-
Coping stones are a cap that sits on top of a wall or structure. They are typically placed on top of a parapet wall or party wall to protect the masonry from weather damage and provide a finished appearance and can be made from stone, slate, brick or capping systems made from metal or other materials.
-
Floors constructed from concrete or similar, sometimes topped with a screed. These are normally ground floors in domestic housing but could be used as intermediate floors in apartment blocks.
-
Timber, metal or a combination floor system normally used as intermediate floors in properties.
-
Any part of a building that is either completely or partially below the normal ground level. Also, can apply to semi- detached or terraced properties built on a hill where floor levels differ from property to property.
-
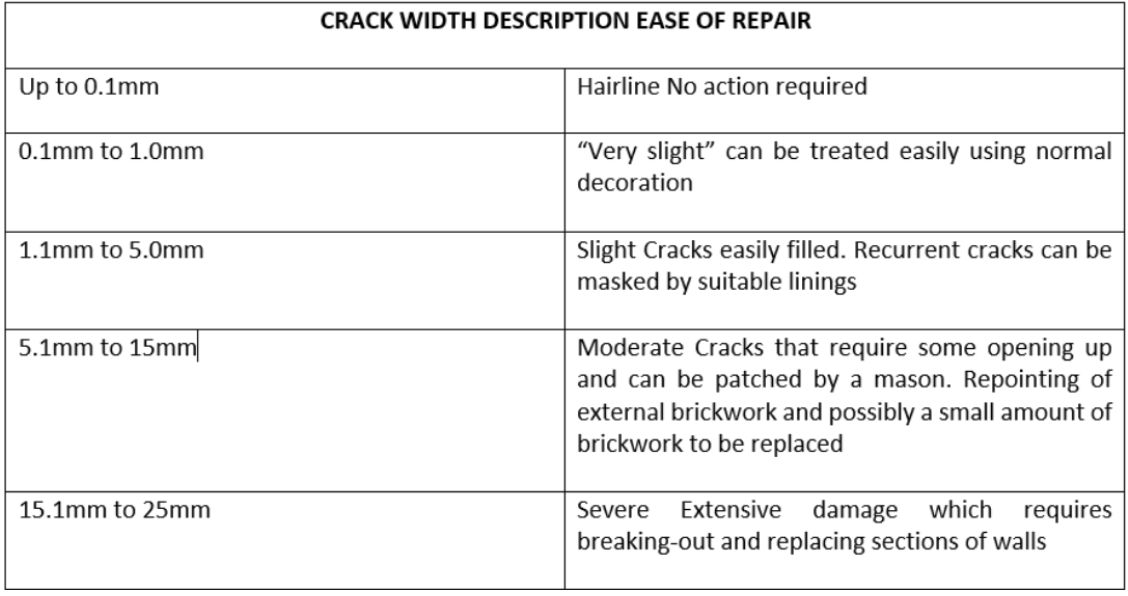
Cracking in buildings can take many forms. It can be cause for concern but in most cases, it is normal and cosmetic only. It can be due to differential movement of materials, thermal movement or in more serious cases structural movement. Cracking may be external only, internal to the plaster finish or both.
BRE Digest 251 Assessment of damage in low rise buildings classifies the severity of cracking based on their crack widths and resultant issues they create.
Diagram showing parts of a property
-
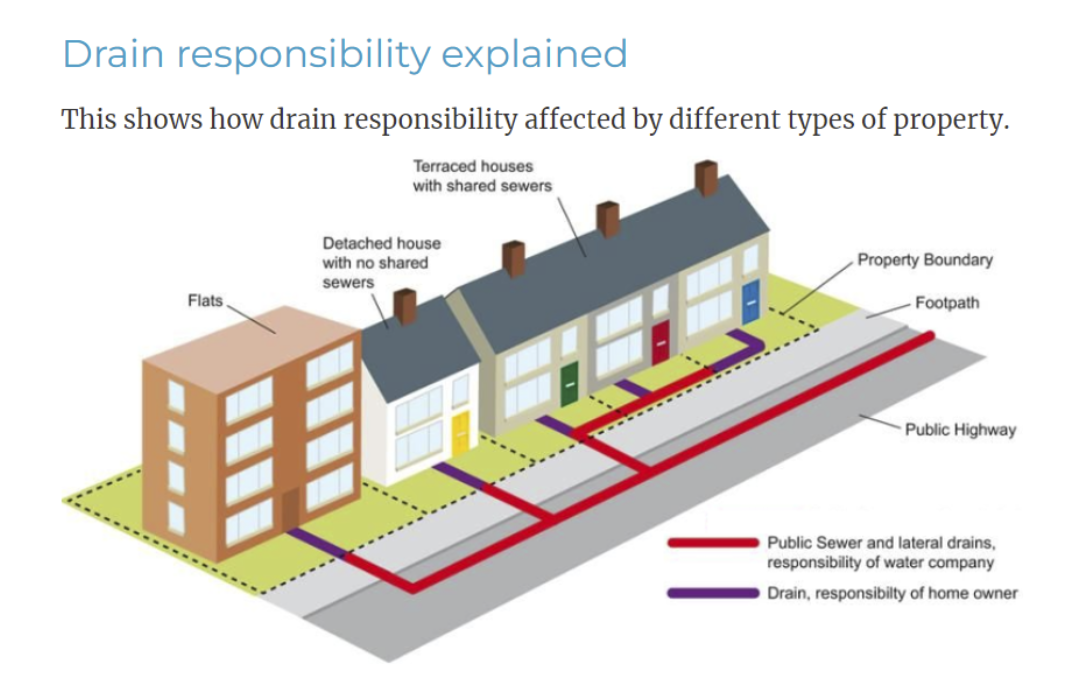
Drainage provides the function to remove foul waste and surface water from the property. Foul drains can either feed directly into the main sewers or can discharge into septic tanks or other systems.
Not all drainage at your property may be owned by you with some drains being the responsibility of the Local Water Authority.
Types of Property and Ownership
-
Apartment blocks are large, multi-unit residential buildings containing multiple apartments or flats within a single structure. They typically feature shared entrances and common areas although not always.
-
Not all properties are “new-build” with some properties being part or all of a conversion or refurbishment of an existing building.
-
A form of property ownership whereby you own the building and the land it is constructed on.
-
A form of property ownership whereby you have a legal agreement with the landlord/freeholder to own the property for a fixed period of time. The document that sets out the terms of the ownership is called the lease. The lease will set out which parts are your responsibility and which parts are deemed common and are the freeholder’s responsibility. Leaseholds do not own the land on which the property is constructed on.
-
Applies to nearly all properties in Scotland including houses and apartments whereby you own the property and the land it is constructed on. With apartments all owners own a share of the freehold and the “Deeds and Conditions” set out where the responsibilities lie and what parts are deemed a common burden.
-
Please note that should the issue you have relate to loss or damage caused by or be consequent upon:
Fire
Lightning
Explosion
Earthquake
Storm
Tempest
Flood
Subterranean fire
Aircraft or other aerial devices or articles therefrom
Escape of Water, Oil or any other liquids from tanks, pipes, heating system or other apparatus
Malicious persons,
Theft and attempted theft,
Impact
Or any accidental cause
You should contact your own Buildings Insurers in the first instance as the above perils are not covered under your Building Warranty.